Time Based Role Example
One of the basic requirements for proper fine-grained authorization is time-based conditions.
On this page, we will learn how to implement temporary role assignments using ABAC Condition Sets in Permit.io, with a step-by-step implementation guide.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure you have the following:
- A Permit.io account.
- A role called
admin. - A resource called
internal_api.
Step 1: Configure Schema & Policy
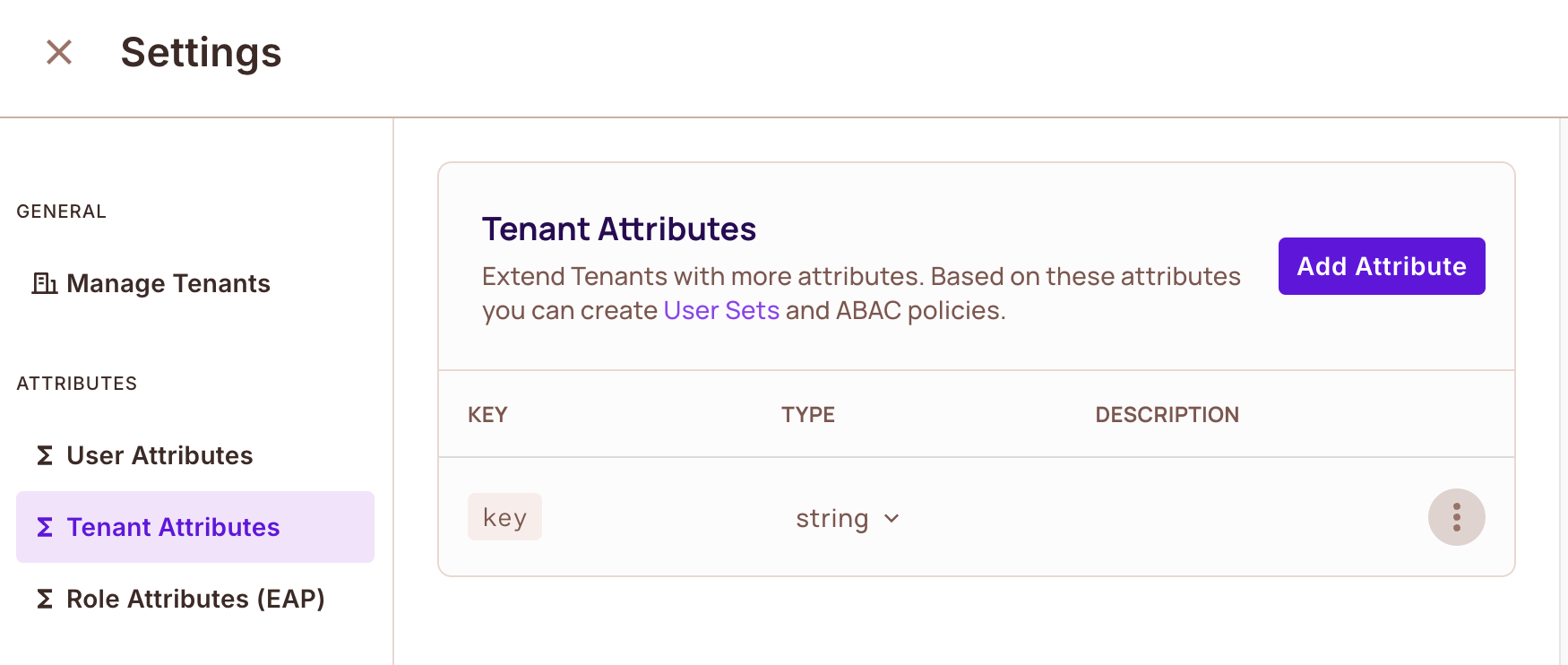
Configure Tenant Attribute Key
- Navigate to Tenant Attributes in the Permit.io dashboard.
- Create a new Tenant Attribute named
key. - Do not assign it to a tenant yet.
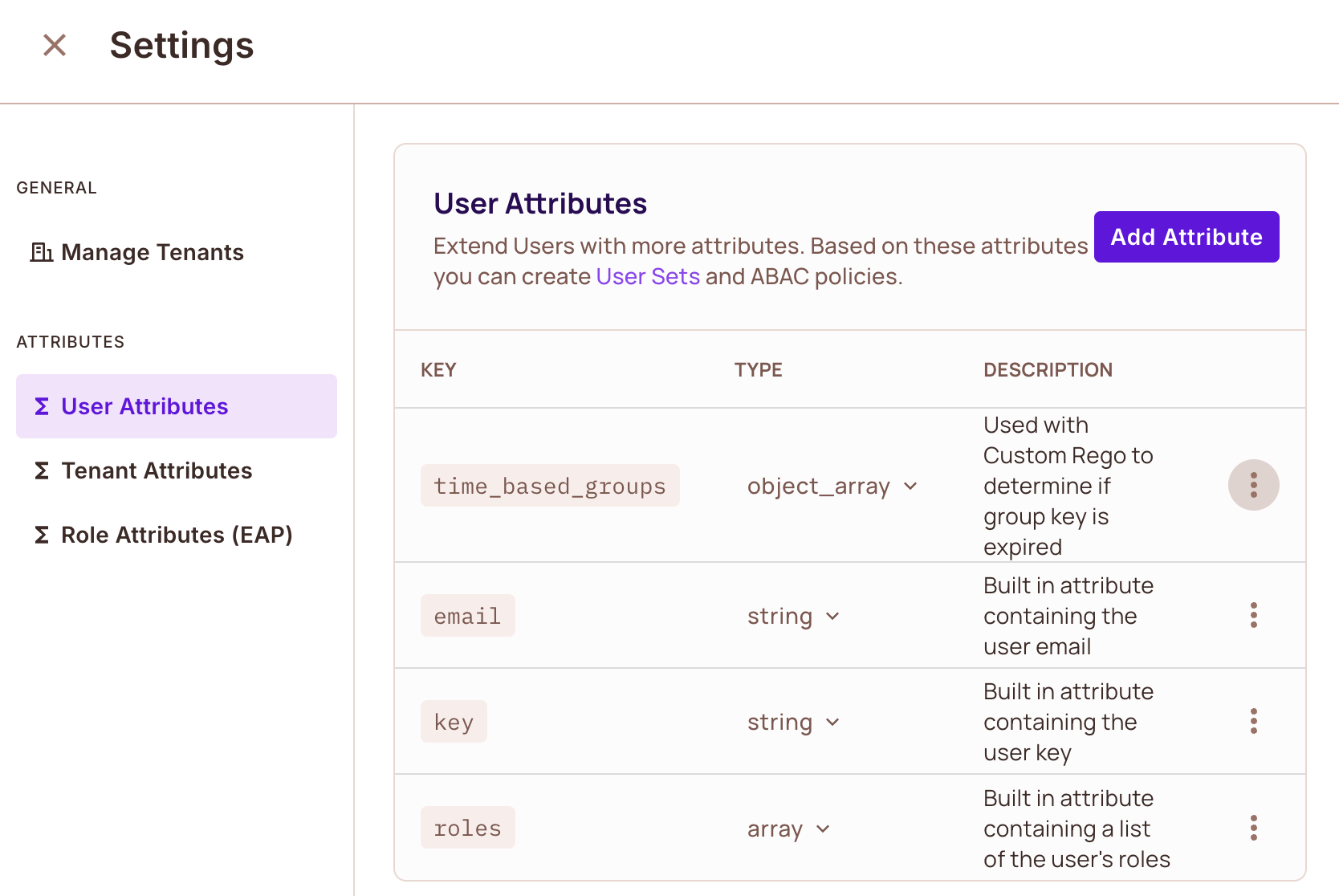
Configure time_based_groups User Attribute
- Go to User Attributes.
- Create the
time_based_groupsattribute. - Do not assign it to a user yet.
Create Condition Set
A condition set ensures temporary permissions based on:
- User role (
admin) - Expiration time
- Tenant key match
Use the following API request to create the condition set:
curl --location 'https://api.permit.io/v2/schema/default/production/condition_sets' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer permit_key_' \
--data '{
"key": "temp-admin",
"name": "Temporary Admin",
"type": "userset",
"conditions": {
"allOf": [
{
"allOf": [
{ "user.roles": { "array_contains": "admin" } },
{ "user.time_based_groups": { "any_match": { "match": {
"expires": { "greater-than-equals": { "ref": "user.current_time" } },
"tenant": { "equals": { "ref": "tenant.key" } }
}}}}
]
}
]
}
}'
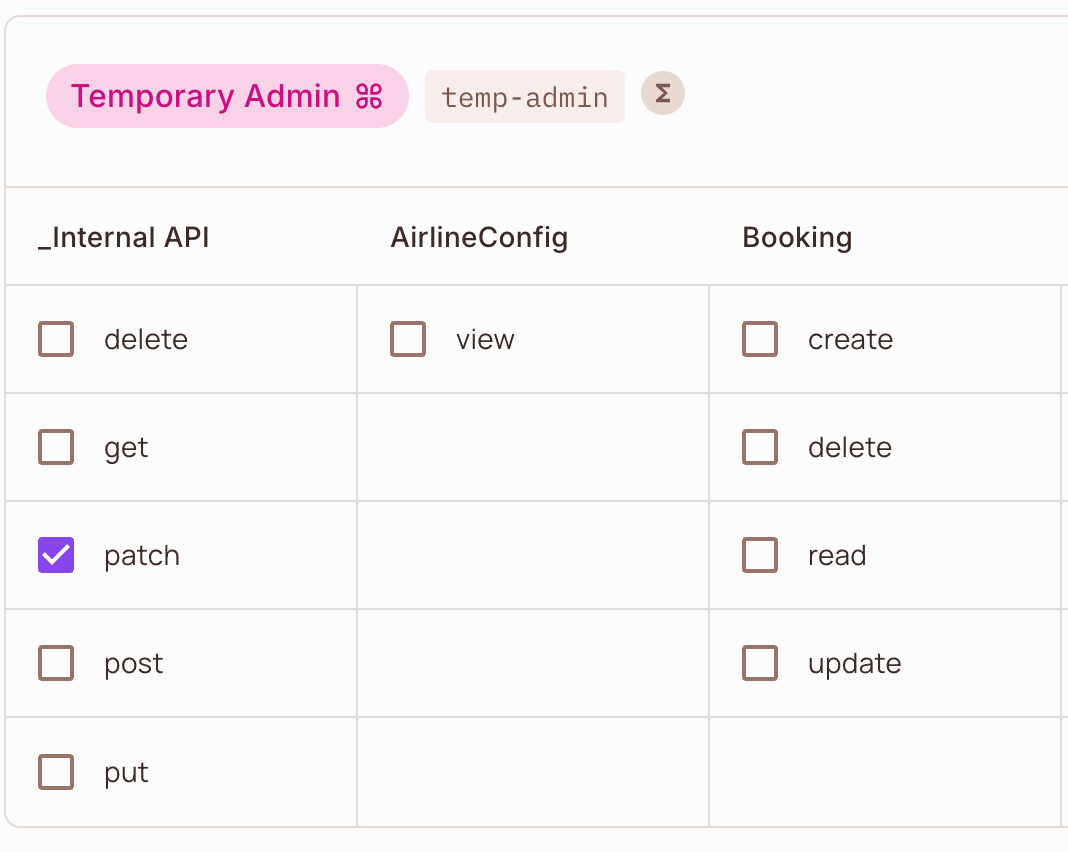
Assign Permissions to the Condition Set
- Navigate to the Policy Editor.
- Assign the necessary resource actions to the
temp-admincondition set.
Step 2: Test the Configuration
Create a User with Role & time_based_groups Value
Assign the admin role and set time_based_groups:
"time_based_groups": [
{
"role": "admin",
"tenant": "default",
"expires": 1733256879832
},
{
"role": "admin",
"tenant": "coke",
"expires": 1733861761081
}
]
The expires value is a Unix timestamp in milliseconds. The current_time value must be passed in permit.check() as a user attribute.
Run Permit Check
Use the following code snippet to verify permissions:
const permitted = await permit.check(
// User object
{
key: "george@test.com",
attributes: {
current_time: new Date().getTime(),
},
},
// Action
"patch",
// Resource
{
type: "_internal_api",
tenant: "coke",
}
);
Modify user.time_based_groups expiration times to test different scenarios.
In a production environment, update User.time_based_groups[] via the Permit.io API dynamically with time.now() + expiration_amount.