The 4-Perimeter Framework
AI applications process vast amounts of data and execute automated actions. Without proper access control, they become vulnerable to unauthorized access, data leaks, and compliance risks.
The Key: Fine-grained authorization (FGA)
FGA ensures that only the right users—and AI agents operating on their behalf—can access and act on data, reducing the risk of AI misuse, prompt injections, and sensitive data exposure.
The new Four-Perimeter Framework is a structured approach to securing AI interactions at every stage, from prompt input to final response.
Prompt Filtering
Prompt Filtering prevents harmful or unauthorized input from reaching the AI model. It applies policy logic before LLMs receive prompts, helping mitigate prompt injection, data exfiltration, and overreach.
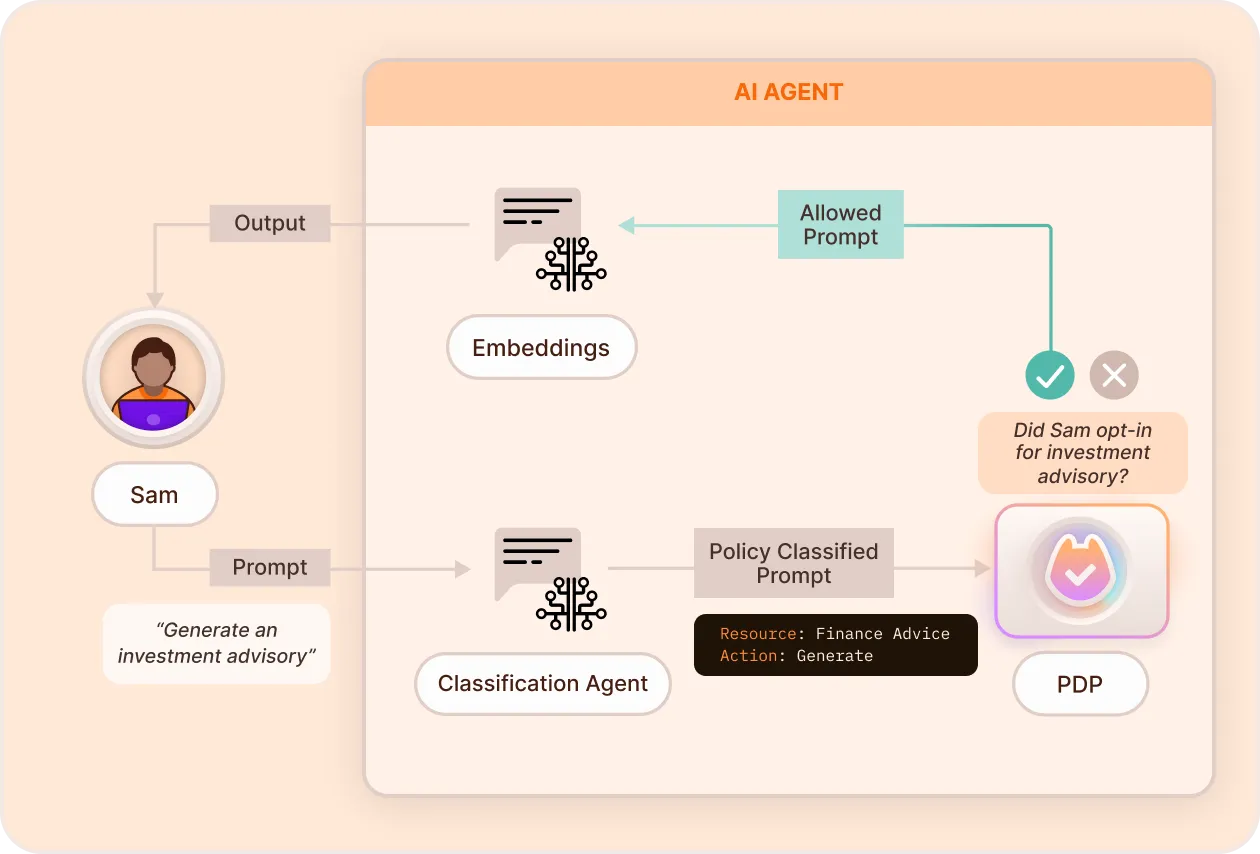
Key Features
- AI-Driven Intent Classification: Utilize OpenAI's language models to understand the user's intent behind natural language prompts.
- Dynamic Access Enforcement: Apply permissions in real-time based on the classified intent and user attributes before prompts reach the AI model.
- Flexible Access Patterns: Handle complex attribute matching and simple validations without hardcoded rules.
- Natural Language Understanding: Allow users to interact using plain English, with the system inferring necessary details.
Further Reading
- Guide: Prompt Filtering with OpenAI: Using GPT for GPT Access Control
- GitHub Repo: permit-prompt-filtering
RAG Data Protection
Secures the retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) layer by filtering access to internal knowledge bases, documents, and vectors. Ensures AI only sees the data it is authorized to retrieve.
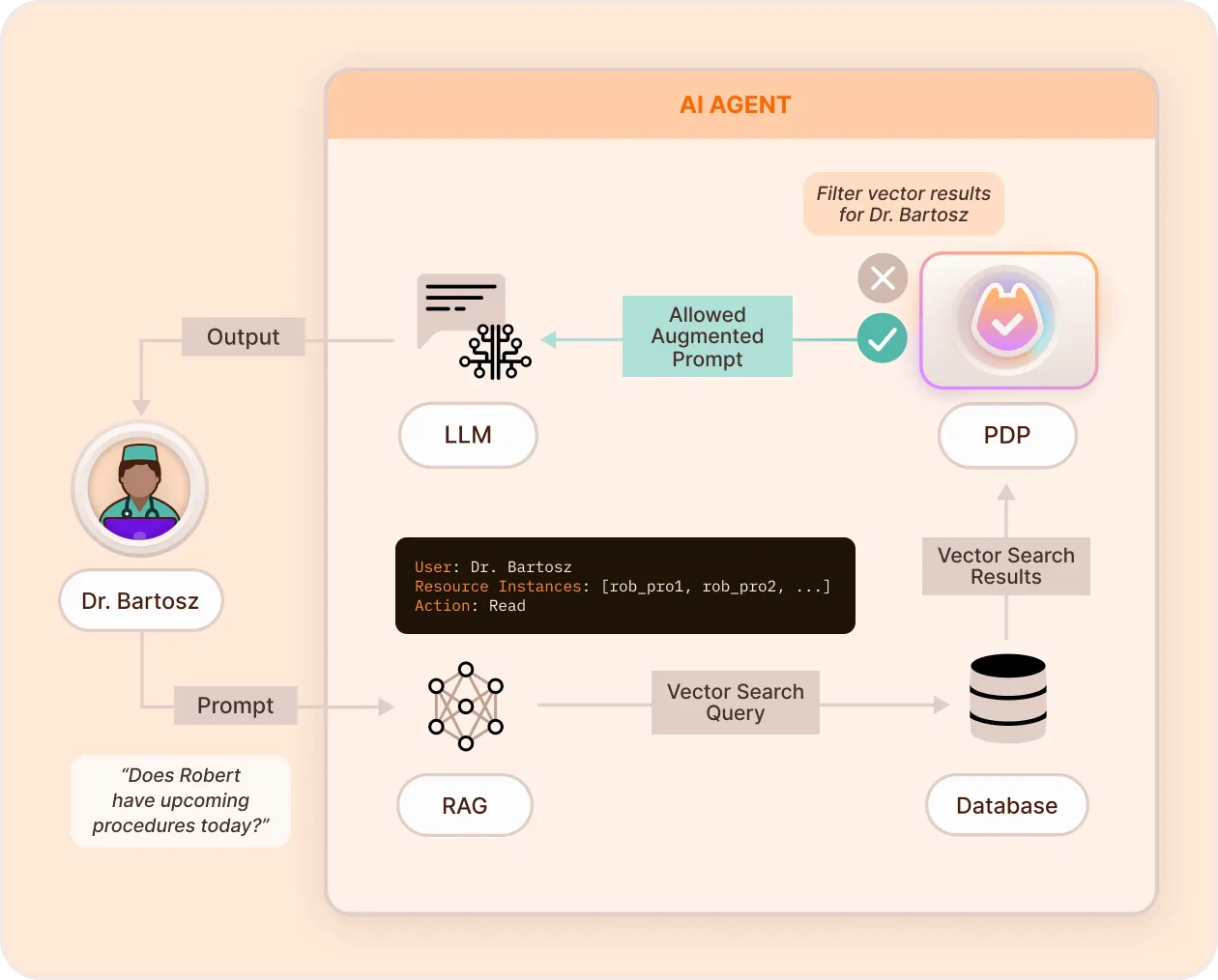
Key Features & Benefits
- Granular Access Control - Define who can retrieve what from vector databases and knowledge bases.
- Fine-Grained Filtering - Prevent unauthorized AI data access by applying attribute-based access control (ABAC) to RAG queries.
- Pre-Query & Post-Query Filtering - Prevent exposing sensitive information by restricting data access before retrieval, or filtering results after processing.
- Seamless Framework Integration - Use Permit's RAG security components in Chain and Agentic frameworks to apply FGA on AI data retrieval.
Further Reading
- Guide: Building AI Applications Using RAG and FGA
- GitHub Repo: permit-mongodb-secure-rag
Secure External Access
Apply policies when AI agents try to perform real-world actions—API calls, transactions, or external service integrations, enforcing identity and limiting what agents can do.
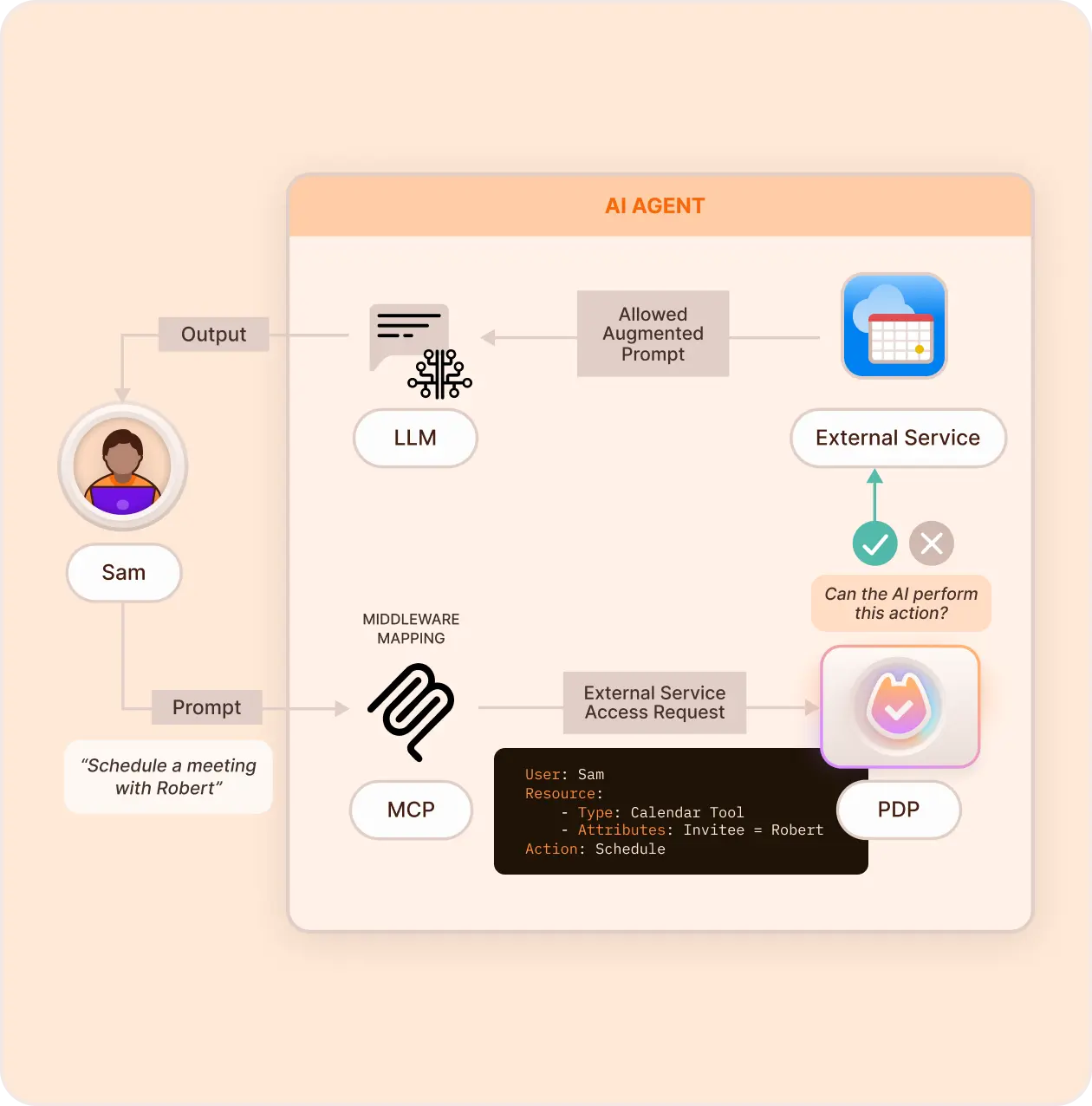
Key Features & Benefits
- Enforce Identity-Based Permissions - Assign machine identities to AI agents to track and manage their access to external tools and resources.
- Define Permitted Actions - Specify which API calls, transactions, and operations are AI-authorized.
- User-Approved Transactions - Require human approval for critical actions (e.g., purchases, bookings, or account changes).
- Approval Flow / Access Request APIs - Enable dynamic approvals and access requests through APIs and embeddable no-code interfaces.
- Access on Behalf - Create traceable, auditable policies for actions made on behalf of human/AI users, with full decision-making chain visibility.
Further Reading
- Guide: Delegating AI Permissions to Human Users with Access Request MCP
- GitHub Repo: permit-mcp
Response Enforcement
Apply policy controls to the AI model’s outputs before they are shown to the user. Prevents overexposure of sensitive data, delivering safe, compliant, context-aware AI responses.
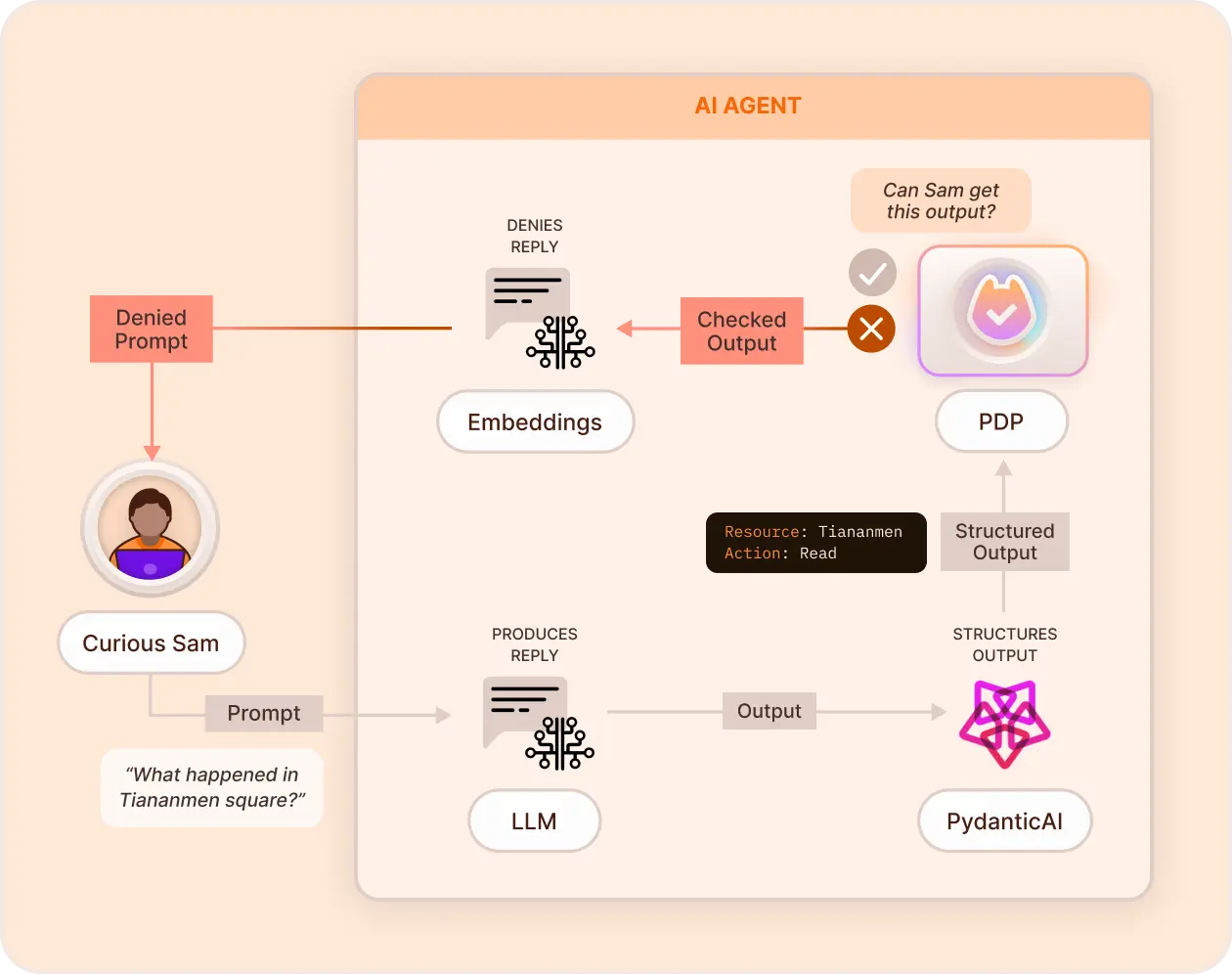
Key Features & Benefits
- Output Filtering - Apply content moderation rules to remove sensitive or inappropriate information before response delivery.
- Compliance Policies - Use classification and access control to ensure AI-generated responses align with pre-determined policies.
- Custom Role-Based Output Control - Define what different user roles can and cannot see in AI-generated responses.
Further Reading
- Guide: Response Enforcement with PydanticAI
- GitHub Repo: Permit-PydanticAI