AWS API Gateway x Permit
This document describes how to create an API Gateway that uses a Permit authorizer to authorize requests.
Create a Permit Authorizer
In order to create an Authorizer that uses Permit, you will need to create a Lambda function that uses Permit to authorize requests.
Create a Lambda Function
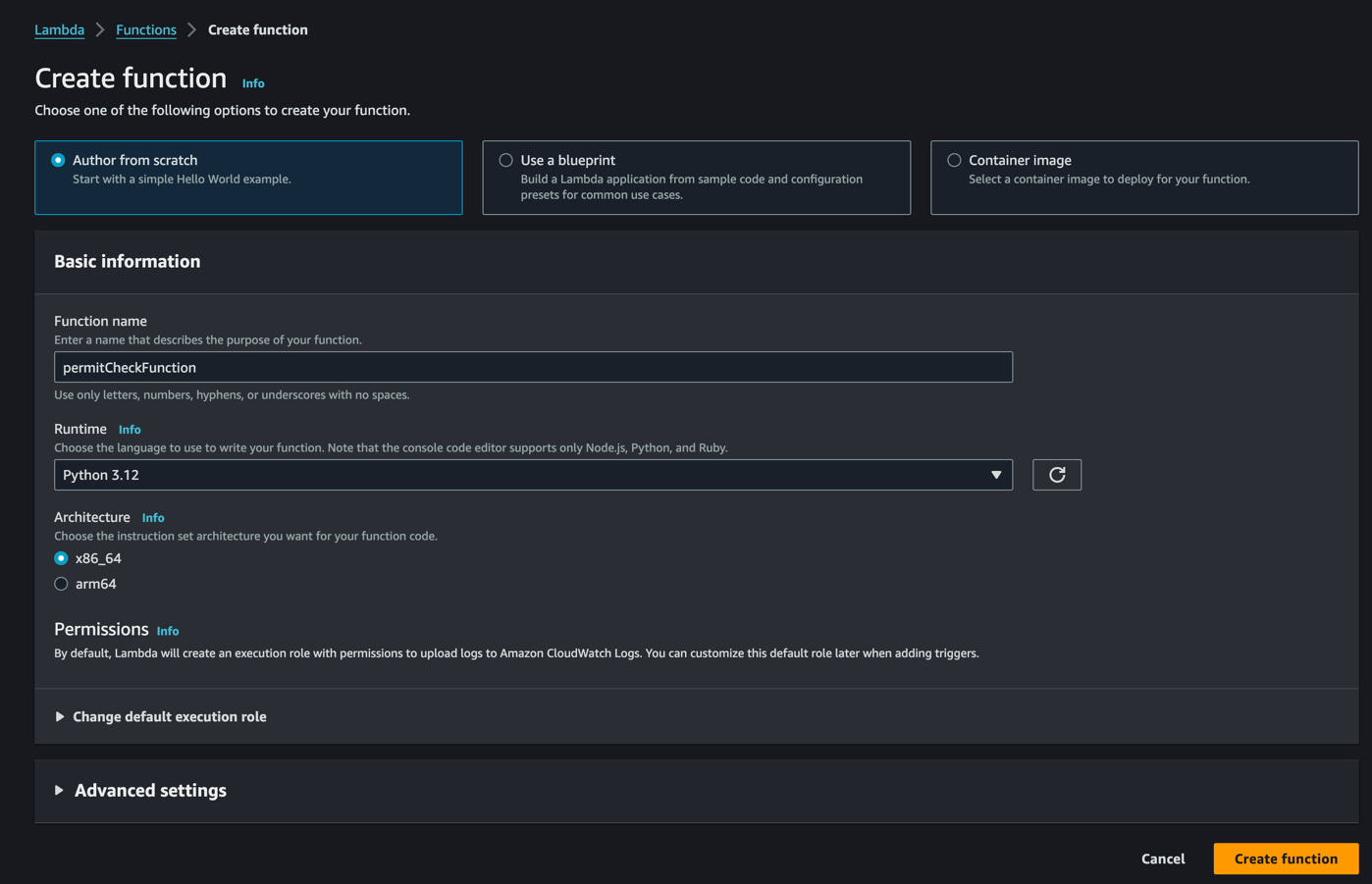
First, create a new Lambda function - we use Python 3.12 in this example but you can use any runtime that Permit supports with one of our SDKs
Create a Layer
Right after this, we'll need to create a layer that contains the Permit library. This is because AWS Lambda does not support the use of external libraries by default.
This step is required only once, and should be on your local environment with python and venv installed.
Create a new directory and a virtual environment -
mkdir permit-lambda
cd permit-lambda
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
Now, install the Permit library -
pip install permit -t python
and create a zip file that contains the library and its dependencies.
zip -r layer python/
Now, you can upload this layer to AWS Lambda.
Upload the Layer
In the AWS Lambda console, click on "Layers" in the left-hand menu, and then click "Create Layer".
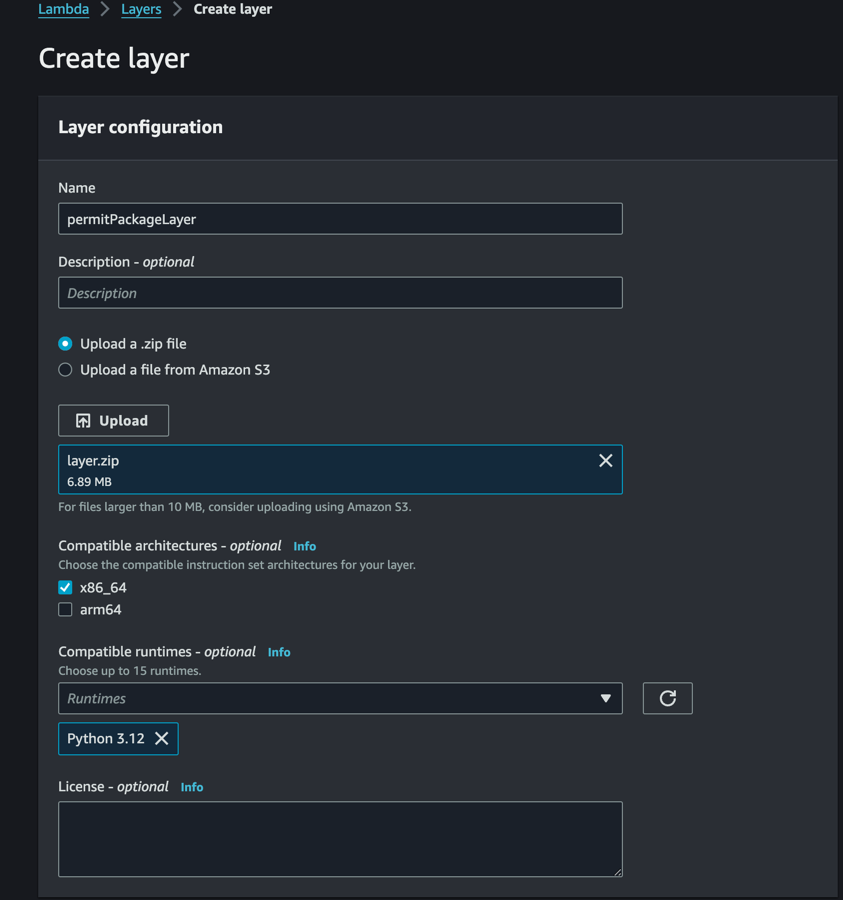
 Upload the zip file you created earlier, and give it a name and description.
Upload the zip file you created earlier, and give it a name and description.
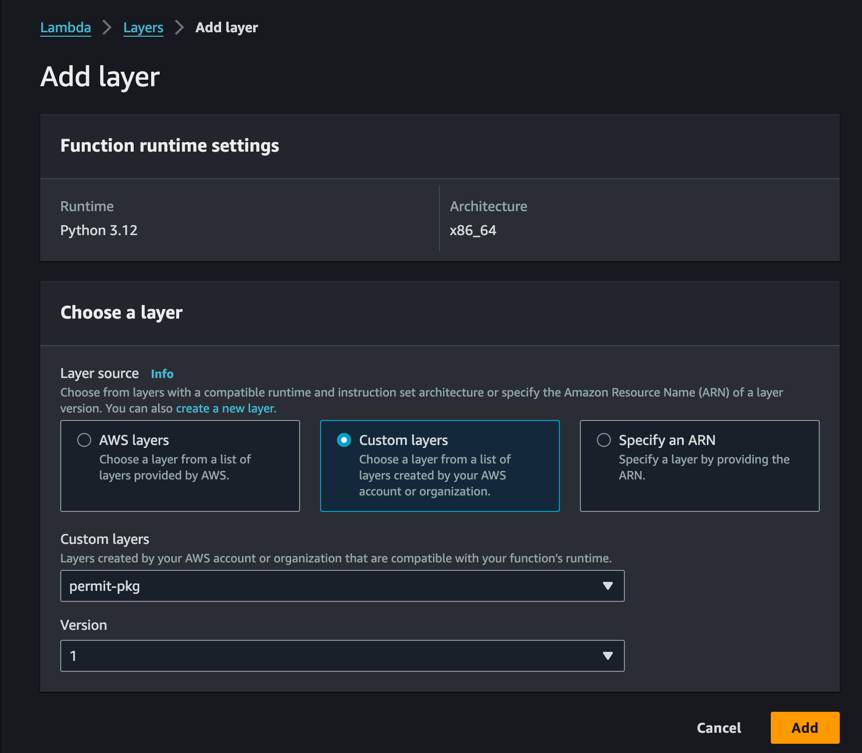
Attach the Layer to the Lambda Function
Going back to the Lambda function, click on the Lambda function you created earlier, and then click on "Add a layer".
Choose the layer you created earlier, and click "Add".
Develop the Lambda Function
Now, you can develop the Lambda function. Here's an example of a Lambda function that uses Permit to check user's permissions -
import asyncio
from permit import Permit
def check_permissions(event, context):
permit = Permit(
pdp="https://cloudpdp.api.permit.io",
token="permit_key_xxxxx", # replace with your API key
)
user = {
"id": event.get("id"),
"email": event.get("email"),
}
return asyncio.get_event_loop().run_until_complete(
permit.check(user["id"], event["action"], event["resource"])
)
You can see in this example few important things:
- Make sure to replace
permit_key_xxxxxwith your actual API key. - We use the Permit library to check the user's permissions, and specifically the
permit.Check()method. - We receive the user's ID, email, action, and resource from the event, and use them to check the user's permissions.
- We are using the Cloud PDP which is hosted by Permit.
Cloud PDP does not support ABAC – it supports RBAC and ReBAC policy models. - Before going to production, please read the detailed capabilities and limits of the Cloud PDP here and the documentation on how to deploy your own PDP to choose the deployment that best suits you.
Note: We use the asyncio library to run the permit.Check() method, as it is an asynchronous method.
Deploy the Lambda Function
Once you have developed the Lambda function, you can deploy it by clicking "Deploy" in the top right corner of the Lambda function page.
Create an API Gateway
Now that you have created a Lambda function that uses Permit to authorize requests, you can create an API Gateway that uses this Lambda function as an authorizer.
Create a New API Gateway
In the AWS console, go to the API Gateway service, and click "Create API". Choose your desired API type, and click "Create API" - we will use the HTTP API in this example.
Create a New Authorizer
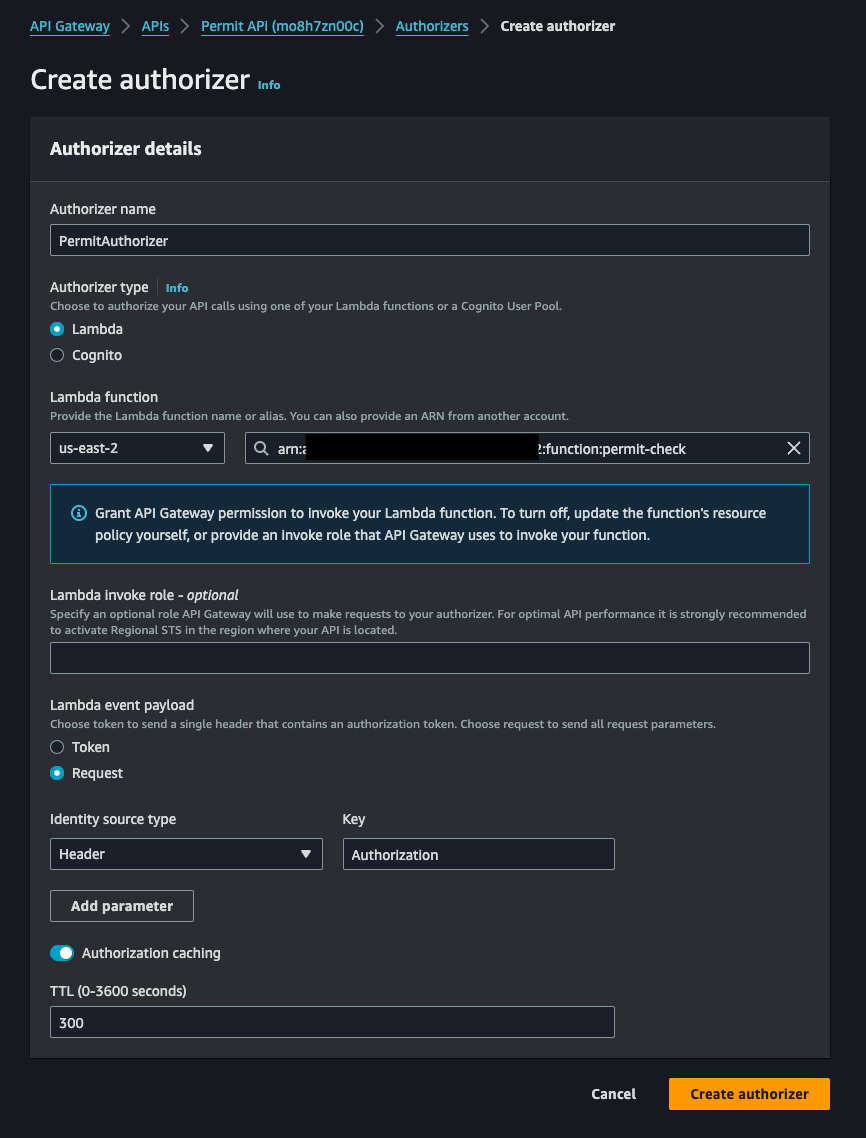
In the API Gateway console, click on "Authorizers" in the left-hand menu, and then click "Create Authorizer".
Choose the Lambda function you created earlier, and choose the event payload version you want to use - we will use the Request - header version in this example.
Attach the Authorizer to a Resource
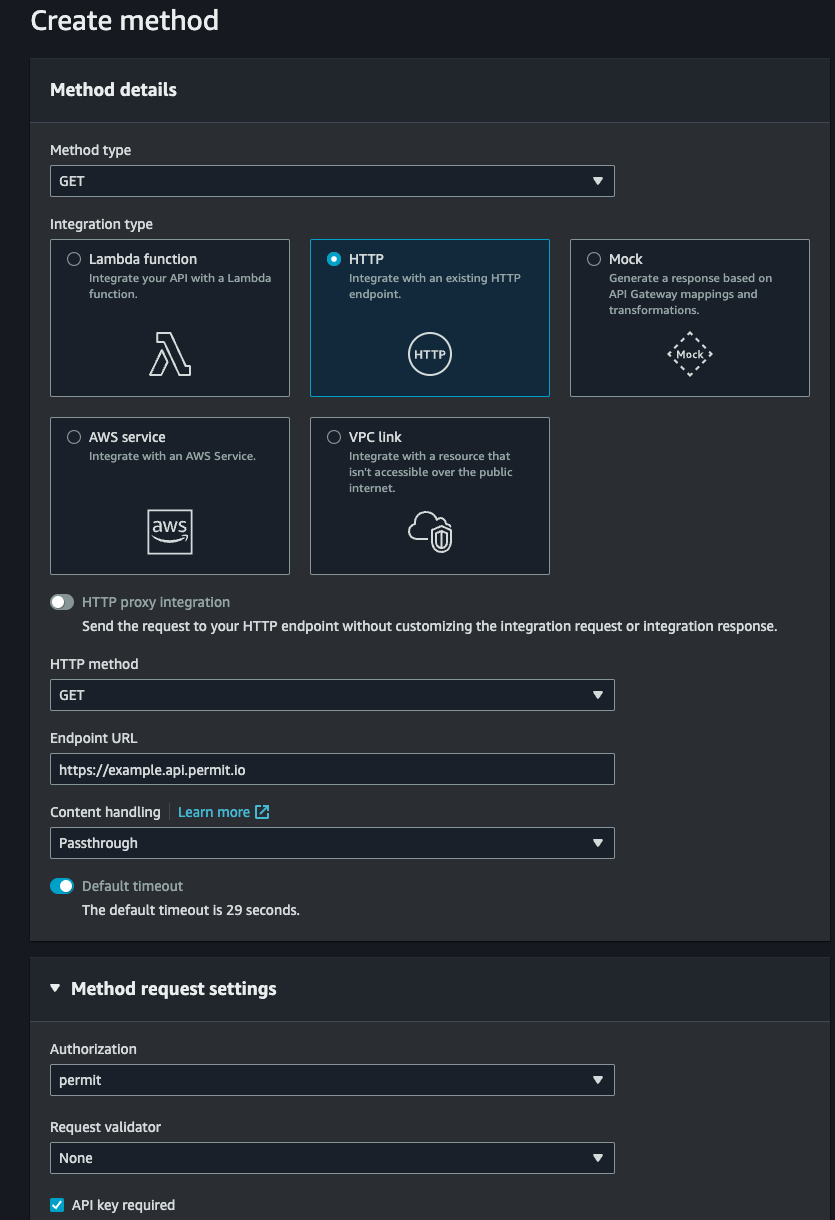
Now, you can attach the authorizer to a resource in your API. Click on "Resources" in the left-hand menu, and then click on the resource you want to attach the authorizer to.
Then, create a new method for the resource, and choose the authorizer you created earlier.
 After you have created the method, you can deploy the API by clicking "Deploy" in the top right corner of the API Gateway console.
After you have created the method, you can deploy the API by clicking "Deploy" in the top right corner of the API Gateway console.
Test the API
Now, you can test the API by sending a request to the endpoint you created. You can use the "Test" tab in the API Gateway console to send a request to the endpoint, and see the response from the Lambda function.
Advanced Usage
More Complex Policies and Checks
In the above example we showed how to check RBAC policy - which is a common use case. However, Permit supports more complex policies and checks, such as ABAC and ReBAC. You can use Permit to check these policies and checks in your Lambda function, and use the result to authorize requests in your API Gateway.
- When using the Cloud PDP, you can use RBAC and ReBAC policies.
- When you need ABAC policies evaluated from this Lambda, you should deploy and point the SDK to a local/container PDP instead of the Cloud PDP.
Read more about enforcing attributes and enforcing relationships in our documentation.
Deploying the PDP to Production
In the above example we used the Cloud PDP, which is hosted by Permit. In production, you should deploy your own PDP, and use it in your Lambda function to check user's permissions. Moreover, it's recommended to deploy the PDP in the same region and VPC (if applicable) as your Lambda function, to reduce latency and improve security.
Read more about deploying the PDP to production and visit our cloud hosts deployment guides in our documentation.