QuickStart - Add permissions to your Node JS app
In this tutorial, we will show you how to integrate Permit.io with your Application in just a few simple steps.
Setup your PDP (Policy Decision Point) Container
We provide you with a Policy-Decision-Point - aka an authorization microservice, as a container for you to use. Please follow the steps below to install and run the container on your local machine.
1. Pull our PDP container from Docker Hub
If you do not have Docker installed as of yet, click here to install Docker.
docker pull permitio/pdp:latest
2. Get the Permit.io API key
Navigate to the Project Management page with the Permit.io web interface. Find the active environment that is marked with a green dot on the icon. Copy the Secret Key.
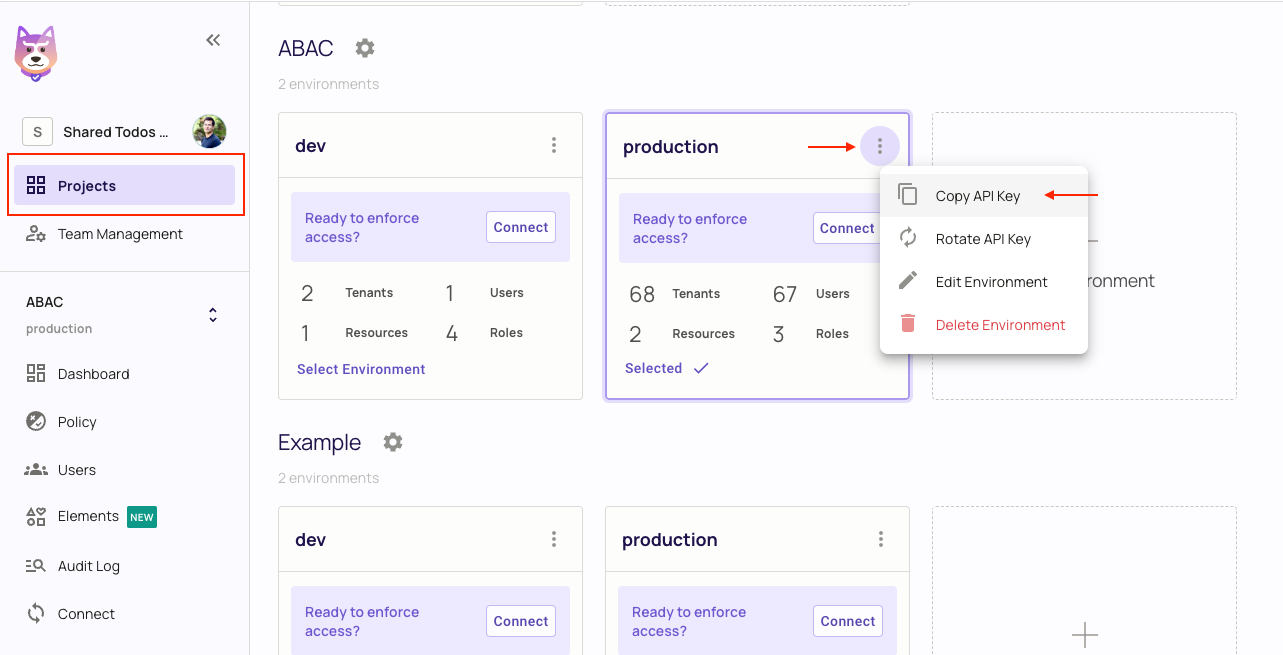
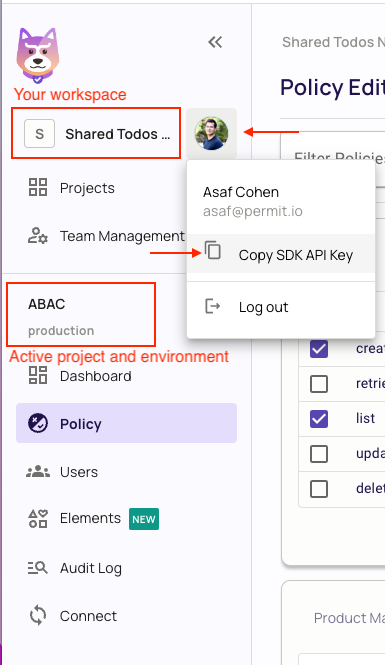
Alternatively, while anyhwere on the Permit.io web interface, click on your user icon in the top right of the screen, and "Copy SDK Secret Key" from there.
3. Run the container
Remember to replace <YOUR_API_KEY> with the Secret Key you have just obtained in the previous step.
docker run -p 7766:7000 --env PDP_API_KEY=<YOUR_API_KEY> permitio/pdp
Congratulations! You should now have a PDP container running. You can always check the status of the container
by typing docker ps in your terminal.
Let's now add the Permit SDK to your app or use the following demo example below.
Add the SDK to your JS code
Initialise the Node.js SDK and check for permissions.
- Install the Permit.io SDK
npm install permitio
- Import the SDK into your code
const { Permit } = require("permitio");
- Create a new instance of the SDK.
You can find instructions on getting a secret API key in the previous section.
// This line initializes the SDK and connects your Node.js app
// to the Permit.io PDP container you've set up in the previous step.
const permit = new Permit({
// in production, you might need to change this url to fit your deployment
pdp: "http://localhost:7766",
// your API Key
token: "[YOUR_API_KEY]",
});
Check for permissions using the API
You can run a permission check with permit.check(), passing in 3 arguments:
user.id: a unique string id that identifies the user doing the action.action: the action performed.resource: the resource (object) the action is performed on.
In the following example we are checking that a user with the unique id john@smith.com can create a document resource.
const permitted = await permit.check("john@smith.com", "create", "document");
if (permitted) {
console.log("User is PERMITTED to create a document");
} else {
console.log("User is NOT PERMITTED to create a document");
}
Permission checks are being run against the PDP container with minimal latency and without leaving your network.
Full app example
Assuming a Node.js app made up of a single file, with the permitio and express modules installed.
const { Permit } = require("permitio");
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
const port = 4000;
// This line initializes the SDK and connects your Node.js app
// to the Permit.io PDP container you've set up in the previous step.
const permit = new Permit({
// in production, you might need to change this url to fit your deployment
pdp: "http://localhost:7766",
// your secret API Key
token: "[YOUR_API_KEY]",
});
// You can open http://localhost:4000 to invoke this http
// endpoint, and see the outcome of the permission check.
app.get("/", async (req, res) => {
// Example user object
// You would usually get the user from your authentication layer (e.g. Auth0, Cognito, etc) via a JWT token or a database.
const user = {
id: "[A_USER_ID]",
firstName: "John",
lastName: "Doe",
email: "johndoe@permit.io",
};
// check for permissions to a resource and action (in this example, create a document)
const permitted = await permit.check(user.id, "create", "document");
if (permitted) {
res
.status(200)
.send(
`${user.firstName} ${user.lastName} is PERMITTED to create document!`
);
} else {
res
.status(403)
.send(
`${user.firstName} ${user.lastName} is NOT PERMITTED to create document!`
);
}
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Example app listening at http://localhost:${port}`);
});